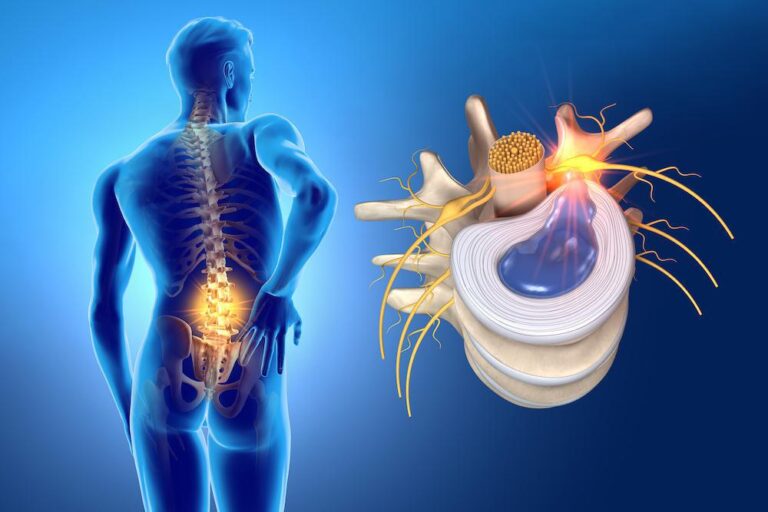
Herniated discs are a common and painful condition that affects many people worldwide. They occur when the gel-like core of an intervertebral disc herniates or shifts, putting pressure on surrounding nerves and causing symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness. While medical treatment may be necessary in some cases, physiotherapy plays a crucial role in pain relief and rehabilitation. In this article, we will explore what herniated discs are and provide practical advice for physiotherapy patients to effectively manage this condition.
What is a Herniated Disc?
The vertebrae of our spine are separated by intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers and allow movement. A herniated disc happens when the nucleus pulposus (the inner gel) of one of these discs moves out of its normal position and compresses the nearby nerves. This can be due to injury, wear and tear, or degeneration over time. Herniated discs are most common in the lumbar region (lumbar hernia) and cervical region (cervical hernia).
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc:
Symptoms vary depending on the location and severity of the herniation. Patients may experience:
- Lower back or neck pain radiating to the legs or arms.
- Numbness or tingling in the affected limbs.
- Muscle weakness in the impacted areas.
- Difficulty walking or maintaining certain postures.
How Physiotherapy Can Help You
Physiotherapy plays an essential role in managing herniated discs and can offer significant benefits to patients. Common therapeutic approaches include:
- Manual Therapy: Physiotherapists use manual techniques to relieve pressure on nerves and improve spinal mobility. These may include massage, gentle spinal manipulations, and targeted stretches.
- Strengthening Exercises: Therapeutic exercises to strengthen the abdominal, lumbar, and paravertebral muscles can help stabilize the spine and reduce pressure on the herniated discs.
- Spinal Traction: Traction techniques are used to gently separate the vertebrae and reduce pressure on the discs, which may alleviate pain and improve function.
- Hydrotherapy: Warm water therapy can provide relief and relaxation to affected muscles and joints, aiding recovery.
- Posture and Movement Education: Physiotherapists teach patients how to maintain proper posture and perform safe movements to prevent flare-ups and promote spinal health.
Practical Advice for Physiotherapy Patients
- Follow the Treatment Plan: Carefully adhere to the treatment plan prescribed by your physiotherapist, including personalized exercises and therapies.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: During recovery, avoid activities that put extra strain on your spine, such as heavy lifting or high-impact sports.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to therapy and exercises, and communicate any concerns or changes in symptoms to your physiotherapist.
- Maintain an Active Lifestyle: While avoiding high-impact activities, staying active with low-impact exercises can support your recovery.
Physiotherapy is an effective and non-invasive approach to treating herniated discs. Through specialized techniques and personalized therapy, physiotherapists can help relieve pain, improve mobility and function, and speed up recovery. It is essential to follow your physiotherapist’s recommendations and actively participate in your recovery process to achieve the best possible results. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any treatment program.