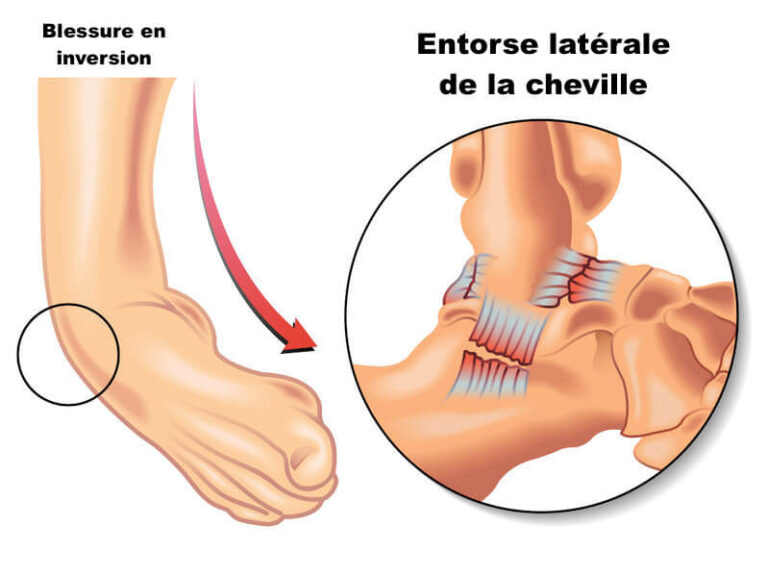
An ankle sprain is a common injury that affects people of all ages and activity levels. It occurs when the ligaments connecting the bones of the ankle stretch or tear due to a twist or sudden movement. This injury can vary in severity, ranging from mild strains to complete ligament tears. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures for ankle sprains.
Causes:
An ankle sprain typically happens when the foot suddenly rolls inward or outward, putting excessive pressure on the ankle ligaments. This can occur during sports activities, walking on uneven terrain, tripping, or simply taking a wrong step.
Symptoms:
Typical symptoms of an ankle sprain include sharp pain, swelling, bruising, difficulty moving the ankle, tenderness to touch, and in severe cases, instability when bearing weight. It is essential to seek medical care if the pain is severe, if there is an obvious deformity, or if you are unable to bear weight on the ankle.
Grades of Sprain:
Ankle sprains are classified into three grades based on severity:
- Grade I: Mild ligament stretch.
- Grade II: Moderate stretch and partial ligament tear.
- Grade III: Complete ligament tear, leading to ankle instability.
Treatment:
Proper treatment is crucial for full recovery and to prevent long-term complications. The following steps can aid recovery:
- Rest and Protection: Rest the ankle and avoid activities that worsen the injury. Using braces or bandages can provide additional support and protection.
- Ice: Apply ice to the affected area for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 to 3 hours during the first few days to reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage to control inflammation and stabilize the ankle.
- Elevation: Keep the ankle elevated above heart level while resting to reduce swelling.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation when taken as directed.
- Rehabilitation: Once swelling and pain decrease, start a program of exercises and physical therapy to strengthen the ligaments and restore mobility.
Prevention:
To prevent ankle sprains, consider these preventive measures:
- Warm-up: Perform warm-up exercises before engaging in sports or intense physical activity.
- Proper Footwear: Wear well-fitting shoes that provide good ankle support.
- Muscle Strengthening: Keep the muscles around the ankle strong and flexible to help prevent injuries.
- Safe Terrain: Be cautious when walking or running on uneven or slippery surfaces.
- Avoid Overuse: Recognize your physical limits and avoid overstraining the ankle.
Conclusion:
Ankle sprains are common but treatable injuries. With proper care and following medical advice, most people can fully recover and return to their normal activities. It is always important to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and to rule out more serious injuries if an ankle sprain is suspected. Prevention also plays a key role in maintaining ankle health and integrity.